This section describes typical workflows and Elastic Access behavior for different scenarios:
- Elastic Access Workflow When Using One-Off Requests
- Elastic Access Workflow When Using Sessions
- Producer Tasks Vs. Customer Tasks
- Behavior When Tokens are Charged to Multiple Line Items
- Behavior When Invalid Items are Requested
- Behavior When Line Item Status Changes in the Back Office
- Behavior When Insufficient Tokens Are Available for Automatic Charge
The examples and descriptions related to sessions on this page assume the standard automatic charge interval of one hour. However, the automatic charge interval can be configured for anything from 10 minutes to 24 hours. Refer to the section on Configuring the Automatic Charge Interval for more information.
The following diagram depicts the steps of an Elastic Access workflow (using one-off access requests), using the example product PhotoPrint.
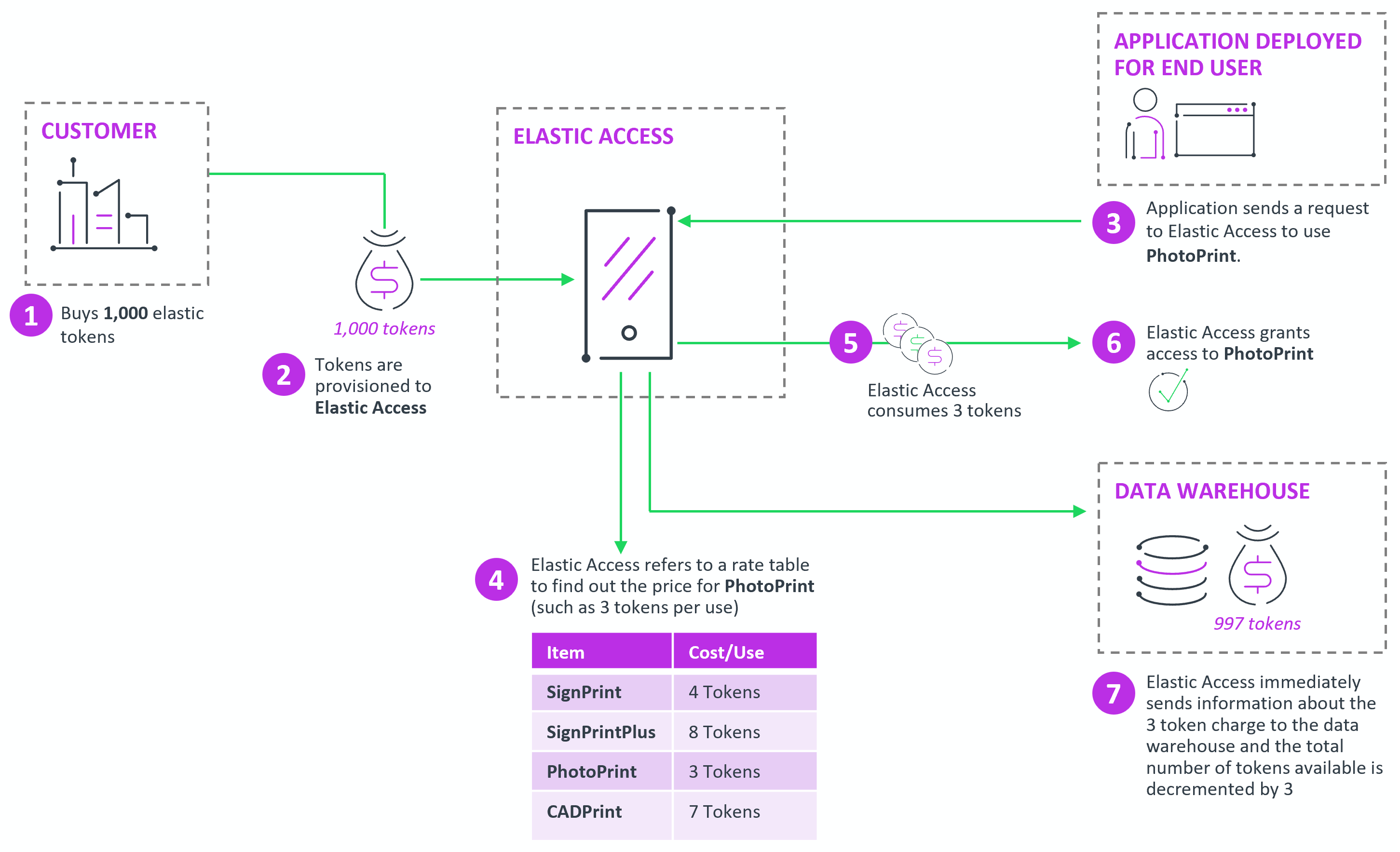
The basic workflow consists of calls to the /sessions REST APIs, which are initiated by the client application. The calls are described in the following table.
| API Call | Session status | Client Application Activity | Elastic Access Service Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| POST /api/<version>/sessions | IDLE | Initiate a session. | None. |
| PUT /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId} | ACTIVE | Make access requests for items during a session at any time, repeatedly. | Keep record of items that client application is using. Make automatic charge every hour. Send usage and automatic charge information to data warehouse. |
| GET /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId}/heartbeat | ACTIVE | Send heartbeat within 30 minutes of last automatic charge to indicate that item is still being used (otherwise session ends). Client needs to read response. If 204, continue. Any other reponse, close application. See also Sending a Heartbeat. | If no heartbeat received within 30 minutes of last automatic charge, terminate the session. |
| DELETE /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId} | TERMINATED | End the session. | Terminate the session. Make refunds to adjust charge to time; send information to data warehouse. |
The following diagram illustrates the workflow:
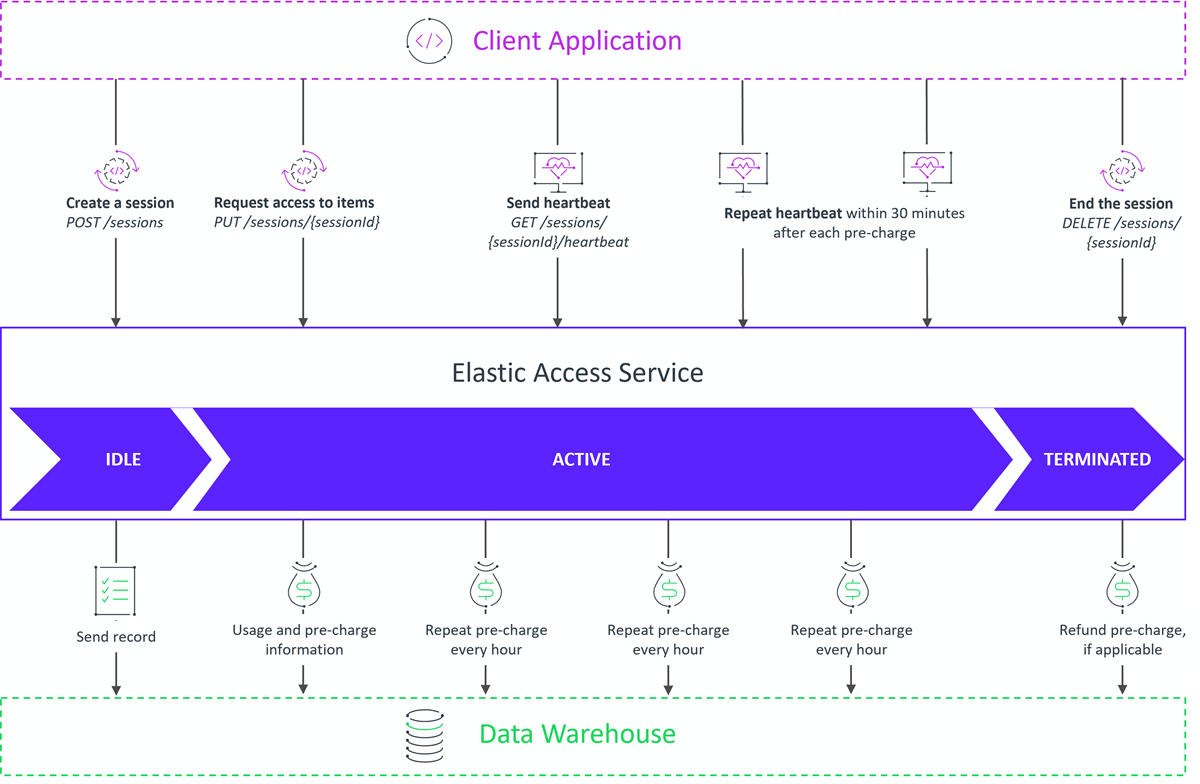
For workflows showing automatic charges and sending a heartbeat, see the sections Automatic Charging Concepts and Sending a Heartbeat, respectively.
This section provides an overview of the tasks that a producer, administrator or client application perform and the corresponding APIs. The task numbers refer to the corresponding tasks in the diagram below the table:
| Persona | Activity | Method | PAS_SessionExHeartbeat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Producer | Implement software to request use of items valid in the rate table, for which tokens will be charged | N/A | N/A |
| Create rate table (task 1) | POST | /provisioning/api/<version>/rate-tables | |
| View instances (task 2) | GET | /provisioning/api/<version>/instances | |
| View line items (task 3) | GET | /provisioning/api/<version>/instances/{instanceId}/line-items | |
| Map line items to an instance (intended for producers who do not use FlexNet Operations as their back office) | PUT | /provisioning/api/<version>/instances/{instanceId}/line-items | |
| Monitor usage data (task 4) | N/A | Data Access APIs, Analytics Dashboard, or Snowflake data query | |
| Administrator of customer organization | Obtain instance ID from producer (task 5) | N/A | N/A |
| View line items on the instance (task 6) | GET | /provisioning/api/<version>/instances/{instanceId}/line-items | |
| Delete sessions to tidy up (if client application hasn’t deleted sessions) (task 7) | DELETE | /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId} | |
| Track live sessions and their status (task 8) | GET | /api/<version>/sessions/{instanceId} | |
| End user of client application | Run the client application. | N/A | N/A |
| Client application | One-off access request for use of items (task 9) | POST | /elastic/api/<version>/instances/{instanceId}/access-request |
| Create a session on its instance (task 10) | POST | /api/<version>/sessions | |
| Request use of items in a session (task 11) | PUT | /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId} | |
| Send heartbeat to the session (task 12) | GET | /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId}/heartbeat | |
| Delete the session (task 13) | DELETE | /api/<version>/sessions/{sessionId} |
The following diagram visually separates the tasks, depending on the persona that actions them: 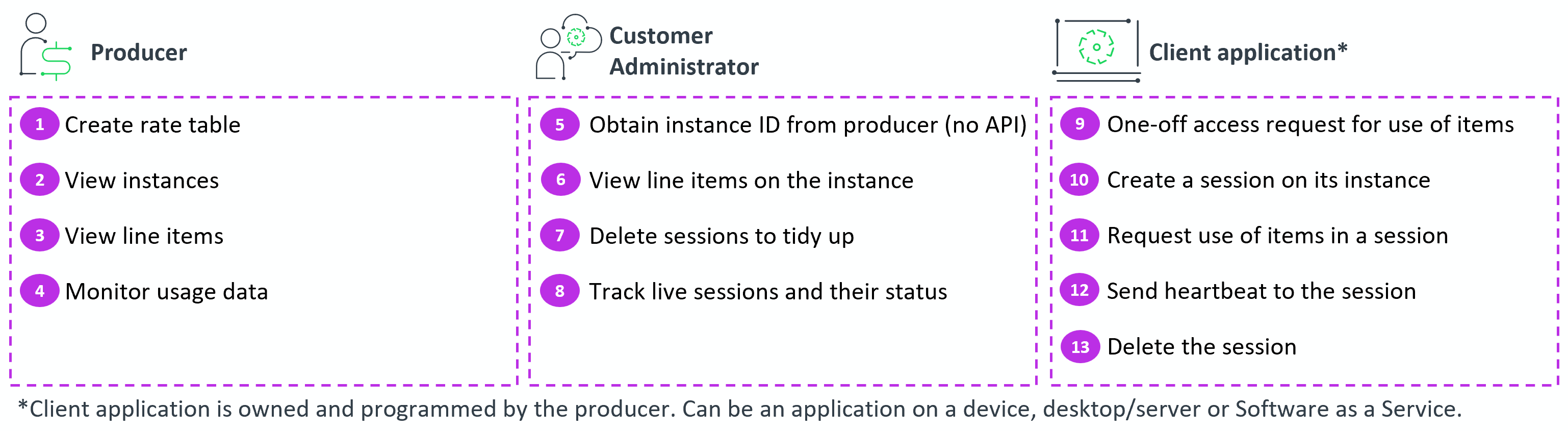
In some scenarios, a line item might not have enough tokens to cover the charges for the requested items. If other line items are available, the charges will be split across multiple line items. This behavior is the same for one-off access requests and session-based access requests. The order in which line items are charged depends on the line items’ expiration and start dates. Tokens are first charged to the line item with the earliest expiration date. If line items have identical expiration dates, the line item with the earliest start date is charged first.
If charges are split across multiple line items for a session-based access request and a refund needs to be made, charges are refunded to the same line items they were charged from.
If multiple items are requested in a session, Elastic Access fulfills all the items, or none of the items. If it is only possible to fulfill some of the items then the entire request fails, and an error response is returned.
The following example illustrates how Elastic Access could charge tokens to multiple line items.
Assume that line items with the following activation IDs have been defined in the Producer Portal:
ACT01-Elastic, quantity: 10, expiration: April 17, 2034ACT02-Elastic, quantity: 100, expiration: August 28, 2035
Example request for a GET call to the /line-items endpoint
[
{
"activationId": "ACT01-Elastic",
"instanceId": "fb1aba68-6af0-43df-a1a3-55f452cb86f0",
"start": 1694437412000,
"end": 1713355200000,
"quantity": 10,
"used": 0,
"attributes": {
"elastic": true,
"rateTableSeries": "PublicationApps"
}
},
{
"activationId": "ACT02-Elastic",
"instanceId": "fb1aba68-6af0-43df-a1a3-55f452cb86f0",
"start": 1694437412000,
"end": 1756382400000,
"quantity": 100,
"used": 0,
"attributes": {
"elastic": true,
"rateTableSeries": "PublicationApps"
}
}
]The rate table specifies the following items:
- PhotoPrint; rate: 3
- CADPrint; rate: 7
Example request for a GET call to the /rate-tables endpoint to retrieve the active rate table:
[
{
"effectiveFrom": 1698849852000,
"created": 1699621714826,
"series": "PublicationApps",
"version": "1",
"items": [
{
"name": "PhotoPrint",
"rate": 3,
"version": "1.0"
},
{
"name": "CADPrint",
"rate": 7,
"version": "2.0"
}
]
}
]The user LisaBarry requests two items:
- 1 count of PhotoPrint, at a rate of 3 tokens per item (3 tokens in total)
- 8 counts of CADPrint, at a rate of 7 tokens per item (56 tokens in total)
Example request for a POST call to the /access-request endpoint to request items:
{
"requester": {
"type": "user",
"value": "LisaBarry"
},
"requestedItems": [
{
"item": "PhotoPrint",
"requestedVersion": "1.0",
"count": 1
},
{
"item": "CADPrint",
"requestedVersion": "2.0",
"count": 8
}
]
}The tokens for PhotoPrint (1 x 3 tokens = 3 tokens) are charged to the line item with activation ID ACT01-Elastic, because this line items has an earlier expiration date than ACT02-Elastic. The number of available tokens for ACT01-Elastic is reduced to 7 (10 - 3 = 7).
The number of tokens for CADPrint (8 x 7 tokens = 56 tokens) exceed the quantity that is now available in ACT01-Elastic (7 tokens). Therefore, 7 tokens are charged to ACT01-Elastic, and the remaining number of tokens is charged to activation ID ACT02-Elastic (49 tokens).
Example response to a POST call to the /access-request endpoint to request items:
{
"correlationId": "5c8ec4fd-f17f-4657-bf09-74a97ddc9f8b",
"requester": {
"type": "user",
"value": "LisaBarry"
},
"requestedItems": [
{
"item": "PhotoPrint",
"requestedVersion": "1.0",
"count": 1,
"status": {
"code": "1001",
"description": "Successfully checked out"
},
"totalTokensCharged": 3,
"lineItems": [
{
"rate": 3,
"activationId": "ACT01-Elastic",
"tokensCharged": 3
}
]
},
{
"item": "CADPrint",
"requestedVersion": "2.0",
"count": 8,
"status": {
"code": "1001",
"description": "Successfully checked out"
},
"totalTokensCharged": 56, #Total quantity charged for CADPrint across line items
"lineItems": [
{
"rate": 7,
"activationId": "ACT01-Elastic",
"tokensCharged": 7 #Quantity of ACT01-Elastic (10 counts) now used up
},
{
"rate": 7,
"activationId": "ACT02-Elastic",
"tokensCharged": 49 #Remaining tokens are charged to ACT02-Elastic
}
]
}
]
}This section describes how Dynamic Monetization handles access requests that include invalid line items.
A line item is invalid if one or more of the following apply:
- The line item is not included a valid rate table.
- The line item’s status is Inactive or Obsolete in the back office.
- The line item was deleted in the back office.
If an access request includes an invalid item among other valid items, a charge for the invalid item cannot be made.
- If this is a standalone access request, all other items are granted if possible.
- If the access request is made to a session, then the entire request fails.
In the following example response for an access request made to a session, the item PhotoAlbum is not included in the rate table and is therefore invalid:
{
"correlationId": "5c8ec4fd-f17f-4657-bf09-74a97ddc9f8b",
"requester": {
"type": "user",
"value": "LisaBarry"
},
"requestedItems": [
{
"item": "PhotoAlbum",
"Version": "1.0",
"count": 1,
"status": {
"code": "201",
"description": "Item not found in any effective rate table"
},
"totalTokensCharged": 0.0,
"lineItems": []
},
{
"item": "PhotoPrint",
"requestedVersion": "1.0",
"count": 5,
"status": {
"code": "102",
"description": "No Status"
},
"totalTokensCharged": 0.0,
"lineItems": []
}
]
}When a line item’s status changes in the back office to Inactive or Obsolete, or when a line item is deleted in the back office, client applications can no longer consume tokens from such line items. Dynamic Monetization allows refunds to be made to such line items.
This section details the behavior for each line item status.
If a line item is made inactive in FlexNet Operations, Dynamic Monetization does the following:
- No longer allows tokens to be consumed from the line item.
- Allows refunds to be made to the line item (for example, when a second access request is received).
- Continues to allow tokens to be consumed from the line item when its state is returned to Deployed.
If a line item is made obsolete in FlexNet Operations, Dynamic Monetization does the following:
- No longer allows tokens to be consumed from the line item.
- Allows refunds to be made to the line item.
If a line item is deleted in FlexNet Operations, Dynamic Monetization does the following:
- No longer allows tokens to be consumed from the line item.
- Allows refunds to be made to the line item.
- When no sessions are using it, deletes the line item.
Call /provisioning/api/<version>/instances/{instanceId}/line-items using GET to retrieve the line item status: DEPLOYED, INACTIVE, or OBSOLETE.
Once the first set of items has been requested, Elastic Access automatically repeats the charge for those same items once per hour, until one of the following occurs:
- The session is deleted.
- The software fails to send a heartbeat in the required time (see Sending a Heartbeat).
- Insufficient tokens are available to make the automatic charge.
In all cases, the session status changes to TERMINATED and no further access requests are possible. A new session is needed for subsequent activity.